Saturday, January 30, 2010
Introduction To Certifications
In this section you will find Network Certification overview-free resources, exam tutorials, Comptia a+ exam, cissp, cisco exams, microsoft certifications. I have given the general overview of the computer networking certifications. Having knowledge of these certifications, it will be very easy for the visitors to decide their certification of choice. Users will also know the prerequisites of this exam, course outline, level of knowledge, and their expertise after having certified.
You will also be able to learn these things while browsing this website communication tutorials, what is data communication, tech study guides, topologies, computer networking guide, what is data recovery, wireless communication, computer interview questions, network tutorials, microsoft exams, cisco exams online certifications and comptia tutorials.
Network+
Network+ exam by Comptia is designed specifically for the IT professional who have more than nine months experience in the computer network administration. The code of the Network+ exam is N10-003 and it was first introduced in 1997. Till the mid of May 2005, according to Comptia’s announcement, more than 150,000 were Network+ exam certified. Network+ is an entry level exam and it paves the way for the IT professionals in their quest for the more advance certifications like MCSE, CCNA, CCNP etc. There are not prerequisites for this certification. Comptia recommends that you must have the A+ certifications.
Network+ certification is well suited and designed for the network administrators. The topics covered in this exam are media and topologies, standards, protocols, network support and implementations. The Network+ certification shows the candidate’s knowledge of the basic networking fundamentals. Like other Comptia’s certifications, the Network+ certification will not be expired once it is achieved.
SECURTY+
Security+ certification is designed for the IT professionals who have 2 years of experience in the network or systems administration and having the main focus on the security. The code of this exam is SY0101 and it was introduced by Comptia in 2002. Security+ is an entry level test for the most advanced tests like ISC2, CISSP and the SANS. As well as it can also be used as the basis for the some Microsoft certifications. Security+ certification is well suited for the network and security administrators and professionals.
The common topics included in this exam are designing security for a network, security infrastructure, cryptography, authentication, access control, internal and external network attacks and the dealing with the company’s security.
Security+ certifications shows the candidates knowledge of these things and it prepares the candidate to such level that he/she competes with the security breaches and finds some good alternative ways that are helpful in reducing the cost of a security breach. Once this certification is achieved it will never expire just like the other certifications of Comptia.
Microsoft
MCSE
Microsoft Certified Systems Engineer (MCSE) is designed for the professionals who are some requirements of analyzing the business, designing, making infrastructure, and implementing the securities at certain levels. MCSE is based on the Microsoft Windows 2000 platform and Windows NT platform (though many of the NT exams have been obsolete now). The Windows 2003 server has been merged into the MCSE exam.
MCSE certification does not retire but the newer versions are released by the Microsoft after few years. So the candidate has to be upgraded himself/herself with these latest exams. There are no specific requirements for the MCSE certifications. Those candidates who have one year experience in managing a computer network, network or desktop operating systems, will be considered suitable for this exam. Job descriptions and roles including after achieving the MCSE are Systems engineer, Network Engineer, Network Consultant, and Systems Analyst.
There is a 7 exams pass requirement for this certification and the candidates how are holding the MCSE 2000, are required to give 2-upgrade exams. By passing these exams you can achieve Windows Server 2000 MCSE exam.
Cisco
CCNA
Cisco CCNA certification (Cisco Certified Network Associates) is an introductory level exam. The CCNA exam by Cisco systems was designed for the candidates who can install, configure and do administrator of the LAN or WAN networks. CCNA is a prerequisite for the some higher level certifications like CCNP and CCDP. The CCNA exam is valid for the three years. In 2003, Cisco has introduced the two paths of the CCNA exam (INTRO and ICND). Job role for the individuals who are CCNA certified are network administration, system administration and network consultant etc.
CCNP
CCNP (Cisco Certified Network Professional) exam is designed for the candidates who can install, configure and troubleshoot a LAN/WAN network of 100 to 500 computers. The CCNP certification has its prerequisites such as CCNP certification. The topics included in this certification are converged networks, security, VPN, quality of service and broadband technologies like VOIP, DSL, Cable net etc. There is a four, three and two exams path to the CCNP. The CCNP exam is valid for the three years. The job role for a CCNP certified are Network administration, LAN administration, WAN administrator and Network consultant.
ISC2
CISSP
CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) is introduced by ISC2. the ISC2 is a not profit organization and it manages the CISSP exams. A CISSP exam is designed for the candidates who are having minimum four years of experience in the field of Information systems. A bachelor and a Master degree separately, can be a substitute of the one required years for this exam. Also, some lower level certifications like SSCP (Systems Security Certified Practitioner) is also recommended before the CISSP exam.
The CISSP exam is aimed for the IT professionals who want to be Information security professionals, systems security professionals and network security professionals
Thursday, January 28, 2010
Introduction to GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)
In the age of mobile communications, the mobile phones are delivering much more than the voice calls. GPRS is a mobile data communication service that is available to the GSM users of the mobile networks. General Packet Radio Service is a wireless technology that can be used on the GSM enabled devices and it operates at the speed of 115 Kb/s. GPRS technology provides the services like internet, web surfing, video conferencing, online shopping, SMS, MMS and email and push to talk over the cellular networks.
GPRS is a value added service and it provides a wide range of bandwidth that’s why it supports numerous high bandwidth services like video conferencing etc. GPRS services are billed on the per KB/s data transfer basis.
There are some limitations, deployment and operational issues that are related to the quality of service, handset availability, network optimization and charging of service. General Packet Radio Service is supported by the point to point protocol, internet protocol and X.25 connections.
GPRS users are referred to as “always connected” because no prior connection establishing is required such as dialing up a modem etc. A larger number of the subscribed users share the same radio resources and high bandwidth. High data transfer speed is among the major features of the GPRS and theoretically it supports up to 171.2 Kb/s by using all the eight time slots at the same time and it make it relatively less costly as compared to the circuit switched networks. The data packets are splitted into the smaller related packets that are reunited at the receiving end.
It also supports the new applications that were not supported by the circuit switched network due to the speed limitations.
GPRS Requirements
To use the GPRS connection you need the following things.
GSM enabled mobile phone
Subscription to the mobile network that supports GSM/GPRS.
Supported Applications
Following are some of the major applications that are supported by the General Packet Radio Service.
Web browsing
Moving Images
Simple Messaging Service
Files Sharing
Vehicle positioning
Home Automation
Remote LAN access
Emails
Vehicle Positioning
Benefits of GPRS Technology
It supports the minimal upgrade to the existing GSM network.
It supports the larger messages length as compared to the SMS.
It supports the VPN and corporate sites access through internet.
It supports the packet based air interface over the existing circuit switched GSM network.
It supports high speed data transfer in an “always connected” mode.
If want to connect your computer with the GPRS mobile phone then you can do this by the following methods.
Bluetooth
Infrared
Data Cable
GPRS is a commonly used mobile communication technology for almost all mobile phones in all over the world. It is instantly available and relatively less costly mobile communication service.
What is Frame relay?
The data is transferred in frames and they are relayed on the data link layer. The network provides permanent and fast virtual connection PVC. Frame relay provides the service between ISDN and ATM. Over the leased telephone lines, frame relay is used to connect the LAN with the fiber optic backbones and with the WAN. The data is transmitted to the destination by means of permanent of switched virtual circuits. Many virtual circuits can exist across a transmission between because virtual circuits only consume the bandwidth when they transmit the data.
The frame relay circuits are the logical circuits that are created at the time of installation and are not created by the users at their systems. In device that is a part of the frame relay network can operate at a very high speed due to the availability of the more bandwidth. The high performance and the error handing techniques allow frame relay protocol to discard the time consuming error handling techniques. The standards of the Frame relay protocols have been developed by the ANSI and CCITT. The frame relay structure is based on the LAPD protocol.
The header of the frame has the data link connection identifier DLCI and congestion bits. When a network becomes congested i.e. it is not able to transmit any new data it begins to discard the frames and these discarded frames retransmitted so more congestion is produced. To avoid this problem several methods have been developed.
Two bits Forward Explicit Congestion Notification and Backward Explicit Congestion Notification in the header of the frame are used to signal the devices at the user end that congestion has been developed. When congestions occur the FECN is changed to 1 and in this way all the downstream nodes and the attached devices at the user end learn about the congestion in the line. The BECN is changed to 1 in the frame that traveling back to the source of the data transmission. So the source is notified of the congestion in the line and to slow down the transmission until the congestion in the line is minimized.
Frame relay works on the consumer hardware such as router and switches and each switch relays the data to the next switch in frame relay network. Frame relay also work with the meshed network because each endpoint can be connected to the different locations and so on. FR is a cost effective and standardized way of creating a wide area network. Frame relay provides error free high data transmission rate and the speed comes in a number of options such as 56 KB/s, 64 KB/s, 128 KB/s, 256 KB/s, 512 KB/s, 1.5 MB/s, and 2 MB per second.
Introduction to T1/E1/T3
T1 is a special type of fiber optic telephone line and it was developed by AT&T Bell Labs. T1 is the most commonly used digital transmission service in the United States. T1 line is capable of transferring the broadband digital data at very high speed i.e. 1.54 Mbps. T1 is an expensive solution for data transmission as compared to the regular telephone lines. But the prices are tend to decrease as the demand grows. Currently T1 is not cost effective for the home users.
A large number of the businesses in USA, Canada and Japan use T1 lines to connect to the internet. There are different ways to provide T1 transmission such as twisted pair cables, coaxial cable modems, fiber optic systems, common careers and digital radios.
In large networks T1 signals can be boosted up to 100 miles by using the repeaters. In telecommunication terminology, T1 is also known as DS1 and T1/DS1 is a method of connecting the digital communication systems with the telecommunication industry and North America.
E1
E1 is a digital data communication system for the European data transmission format. E1 carries the data signals at the speed of 2 Mbps (Full duplex). E1 and T1 lines can be interconnected with each other for international data transmission.
E1/T1 are used for the leased lines transmission. E1 is ideal for the voice traffic and it can carry 32 voice conversions. An E1 line 32 64-Kbps channels and each channel may be used to send and receive data and voice.
E1/PR1 (Primary rate interface) supports 30 B channels and one D channel. Primary Rate Interface (PRI) configurations are used to receive multiple analog calls from the dial-in traffic and analog-modems.
T3
A T3 line is 30 times faster than the T1 line and it supports the data transfer rate 44 Mbps. A T3 line is equivalent to 28 T1 circuits or lines and a T3 is also called a DS3. T3 is a very high speed data transmission system and it is widely used on the internet.
A T3 is capable of carrying 672 voice circuits. T3 connection is mostly used by the ISPs and corporate offices for permanent, high speed and uninterruptible internet access.
ATM NETWORK TECHNOLOGY
ATM technology integrates voice, data and video at the same time. ATM uses fixed size packets called cells of 55 bytes in length. ATM network is a high speed circuit switched network that is capable of transferring one million signals using ATM protocol. ATM is a connection oriented technology in which logical connections are established for the data communication. ATM is implemented in the WAN and telecommunication sectors. Small data cells are used for communication and ATM is designed for high speed and high traffic networks. ATM cells allow voice, data and video transfer at the same time. ATM operates on the data link layer of the OSI model and it uses UTP/STP, fiber optic or air as a communication medium.
ATM CELL BASE
It is a small unit of 55 bytes fixed length and it contains the users and signaling information in it. It has a header with very limited functionality to reduce the internal buffer and to provide the high speed transfer. ATM cell identify the cells that belongs to the same virtual channels and perform easy routing.
ATM SWITCHING
Various switching technologies have been developed in the past to provide the high speed data transfer and secure communication. ATM switching technology provides high speed data transfer due to the connection oriented technology. ATM switching technology uses the predefined routing table so guarantees the fast data communication.
ATM DEVICES
ATM basically uses two types of devices such as ATM switch and end systems. The function of the switch is to handle the transmission of the cells throughout the network. Switches accept the incoming cells from the ATM end station or another ATM switch. On the other hand, ATM end systems contain the ATM adaptors.
ATM CONNECTIONS
ATM supports two types of connections point to point and point to multi point connections. In the point to point connections, two end systems are connected bi directionally or uni directionally. The point to multi point system connects one source to the number of destinations in uni directional. The source sends the information and switch replicates it to the destinations. Unidirectional network connects two switches. A typical ATM network consists of a set of the switches interconnected by point to point links. Switch support two types of interfaces user network and network node interface. Asynchronous transfer mode technology is designed for the reliability, performance, utilization and QOS and it creates fixed channels and routes when data travels between two points. There are four types of the choice when purchasing a connection.
Constant Bit Rate: It specifies fixed size rate and data is transferred in a steady form. Variable bit rate.
Variable Bit Rate: It provides specified throughput and it is best for videoconferencing.
Available bit rate. It provides guaranteed minimum capacity but high rate is also possible when the network is free.
Unspecified bit rate. It does not provide any fixed throughput level and it is best for the file transfer where delay can occurred.
ATM ADVANTAGES
It provides fixed bandwidth and simple routing is possible due to the connection oriented technology. High bandwidth utilization can be possible so it is the best solution for the telecommunication sector, videoconferencing and QOS. There are some of the disadvantages of this technology such as high cost, cell loss due to the high congestion in the network.
Wednesday, January 27, 2010
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Below diagram, for which we will be going to enable the DHCP service on our Cisco router.
The router will act as a DHCP server for the 192.168.1.0/ 24 network. IP Addresses already assigned to our switch (192.168.1.2) and Server (192.168.1.5) will be excluded from the DHCP pool, which will ensure that they are not given to other hosts to cause an IP address conflict
Router#configure terminal
Router(config) #service dhcp
Now we will be creating DHCP Pool to define the IP Address & other requried parameters that will be given to the clients by the DHCP Server.
Router(config) # ip dhcp pool IP-Pool
Router(dhcp- config)# network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255. 0
Router(dhcp- config)# default-router 192.168.1.1
Router(dhcp- config)# dns-server 202.54.56.30 4.2.2.2
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’ s Local Area Network (LAN); an external attacker only has access to equipment in the DMZ, rather than any other part of the network.
Users of the public network outside the company can access only the DMZ host........ ......
More Info - http://www.networke ducator.com/ demilitarized- zone-dmz. htm
Source - www.NetworkEducator .com
CBT Nuggets Collection Pack 2009
Content :
DVD 01- Cisco
DVD 02- CompTIA
DVD 03-05 - Microsoft
DVD 06- Other & Simulators
Details :
Cisco:
640-863 DESGN Designing For Cisco Internetwork Solutions Exam.rar
CCIE Certification Package.iso
CCIE Video Practice Lab.iso
640-816 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2.iso
640-822 ICND1 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1.iso
642-812 BCMSN Building Converged Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks.iso
642-825 ISCW Implementing Secure Converged Wide Area Networks.iso
642-845 ONT Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks.iso
642-901 BSCI Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks.iso
642-444 CIPT Cisco IP Telephony.iso
642-504 SNRS Securing Networks With Cisco Routers And Switches.iso
642-524 SNAF Securing Networks With ASA Fundamentals.iso
642-533 IPS Implementing Cisco Intrusion Prevention Systems.iso
642-642 QOS Quality Of Service.iso
CompTIA:
A+.iso
iNet+.rar
Linux+_1.iso
Linux+_2.iso
Linux+_Update.rar
Network+.iso
Project+.iso
Security+_1.iso
Security+_2.iso
Server+_1.iso
Server+_2.iso
Microsoft:
70-227 Installing, Configuring, And Administering Microsoft Internet Security And Acceleration (ISA) Server 2000, Enterprise Edition.iso
70-228_1 Installing, Configuring, And Administering Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition.iso
70-228_2 Installing, Configuring, And Administering Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition.iso
70-229 Designing And Implementing Databases With Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Enterprise Edition.iso
70-236 Configuring Exchange Server 2007.iso
70-237 Designing Messaging Solutions With Microsoft Exchange Server 2007.iso
70-238 Deploying Messaging Solutions With Microsoft Exchange Server 2007.iso
70-270_1 Installing, Configuring, And Administering Windows Xp Professional.iso
70-270_2 Installing, Configuring, And Administering Windows Xp Professional.iso
70-271 & 70-272 Microsoft Certified Desktop Support Technician.iso
70-282 Planning, Deploying, And Managing A Network Solution For The Small And Medium-Sized Business.iso
70-284 Implementing And Managing Microsoft Exchange Server 2003.iso
70-285 Designing A Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 Organization.iso
70-290 Managing And Maintaining A Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment.iso
70-291 Implementing, Managing, And Maintaining A Windows Server 2003 Network Infrastructure.iso
70-293 Planning And Maintaining A Windows Server 2003 Network Infrastructure.iso
70-294 Planning, Implementing, And Maintaining A Windows Server 2003 Active Directory Infrastructure.iso
70-297 Designing A Windows Server 2003 Active Directory And Network Infrastructure.iso
70-298 Designing Security For A Windows Server 2003 Network.iso
70-299 Implementing And Administering Security In A Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Network.iso
70-350 Implementing Microsoft Internet Security And Acceleration (ISA) Server 2004.iso
70-400 Configuring Microsoft System Center Operations Manager 2007.iso
70-401 Configuring Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager 2007.iso
70-431 Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Implementation And Maintenance.iso
70-443 Designing A Database Server Infrastructure By Using Microsoft SQL Server 2005.iso
70-444 Optimizing And Maintaining A Database Administration Solution By Using Microsoft SQL Server 2005.iso
70-450 Designing, Optimizing And Maintaining A Database Administrative Solution Using Microsoft SQL Server 2008.iso
70-451 Designing Database Solutions And Data Access Using Microsoft SQL Server 2008.iso
70-528 Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0 - Web-based Client Development.iso
70-620 Configuring Microsoft Windows Vista Client.iso
70-621 Upgrading Your MCDST Certification To MCITP Enterprise Support.iso
70-622 Supporting And Troubleshooting Applications On A Windows Vista Client.iso
70-624 Deploying And Maintaining Windows Vista Client And 2007 Microsoft Office System Desktops.iso
70-631 Configuring Microsoft Windows SharePoint Services 3.0.iso
70-640 Windows Server 2008 Active Directory Configuration.iso
70-649 Upgrading Your MCSE On Windows Server 2003 To Windows Server 2008.iso
77-601 Using Microsoft Office Word 2007.iso
77-602 Using Microsoft Office Excel 2007.iso
77-603 Using Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007.iso
77-604 Using Microsoft Office Outlook 2007.iso
77-605 Using Microsoft Office Access 2007.iso
MOS - Excel 2003.rar
MOS - Outlook 2003.rar
MOS - Powerpoint 2003.rar
MOS - Word 2003.rar
MSP Microsoft Project.iso
Windows PowerShell.iso
Windows Vista First Look.iso
Other:
Agile Project Management.iso
C# C-Sharp.iso
CCA Citrix Certified Administrator.iso
CEH Certified Ethical Hacker.iso
CISA Certified Information Systems Auditor.iso
CISM Certified Information Security Manager.iso
CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional.iso
CIW Certified Internet Web Professional - CIW Foundations.rar
CIW Certified Internet Web Professional - Javascript Fundamentals.iso
CIW Certified Internet Web Professional - Perl Fundamentals.rar
CWNA Certified Wireless Network Administrator.iso
CWNA_Update.rar
CWNE Certified Wireless Network Expert.iso
End User Security.rar
ITIL Information Technology Infrastructure Library.iso
LPIC-1 Linux Professional Institute Certification.rar
LPIC-2 Linux Professional Institute Certification.rar
OCA-DBA Oracle Certified Associate - Database Administrator.iso
PMP Project Management Professional.iso
RHCE_1 Red Hat Certified Engineer.iso
RHCE_2 Red Hat Certified Engineer.iso
SCJP Sun Certified Java Programmer.iso
SSCP Systems Security Certified Practitioner.iso
VBscript Visual Basic scripting.iso
VCP VMware Certified Professional.iso
Wireless#.rar
ZCE Zend Certified Engineer PHP 5.iso
Simulators:
CCNA Router N Switch E Simulator.iso
Windows Server 2003 Network Simulator.iso
ALL
http://hotfile.com/list/132590/89a501a
DVD 01
http://www.filefactory.com/f/2fd5cff619699683/
DVD 02
http://www.filefactory.com/f/55234977959714b4/
DVD 03
http://www.filefactory.com/f/d4b0b1aedbf19302/
DVD 04
http://www.filefactory.com/f/8894427fa6e1e0c9/
DVD 05
http://www.filefactory.com/f/b4b747a8a81e10ca/
DVD 06
http://www.filefactory.com/f/350e205739600bad/
An Example of Subnetting a Class C Network
Let’s say we are subnetting a school’s network. We need 5 separate networks that have 30 computers on each subnet.
First we calculate how many usable subnets we need. Next we will need to determine how many hosts are required. Both of these values can be calculated with the following equations:
Two Important Equations to Remember:
________________________________________
• 1. Usable Subnets = (2^n) – 2 , where N = power of bits assigned
• 2. Usable Hosts = (2^n) – 2 , where N = power of bits remaining
Let’s start with usable subnets. Review the diagram below for a visual example.

If you are wondering what the “-2” part of the equation is for, this is how we account for the two addresses in each subnet we can’t use. We will review what these addresses are for more specifically later on. For now, let’s find out what our usable hosts are!

Alright Already! What’s My Subnet Mask?!
Getting your subnet mask at this point is incredibly easy. Simply take all of your network bits, and add them up. Look at the diagram below for a visual guide.

That’s it! You’re done. You have successfully created a subnet mask that can be used on the school’s network. Keep in mind that every computer must have the subnet mask set in order for them to be on the same network. Also note that since we are using a class C network, the first three octets will always be 255. When subnetting other classes, be sure to keep the network portions in mind.
Summary
Subnetting may not be fun, but it is required for students to know on networking exams. That means you should stay away from subnet calculators until you have grasped the full concept of how to do it yourself. These calculators should only be used as a time saving tool, not a learning tool or way to cheat on homework.
With enough practice, subnetting will become much easier. Class A and Class B networks are a bit trickier, but follow the same example as shown above and it should be quite easy to accomplish.
Subnet Masks

The class B network will need to recognize two network portions, and two host portions. This can be seen in the below diagram.

Lastly, we have the class C subnet. It is the most commonly used subnet, so pay special attention to it in the upcoming lecture. You can see a diagram of the default subnet below.

Classes in Subnet
There are three main types of classifications of IP addresses in IPv4: class A, class B, and class C. There are class D and class E types, but those are for multicasting and private uses, respectively. Each class differs by the number of network and host octets it has. Each network octet is for classifying which network a host is on. More network octets will mean more networks! Likewise, each host octet specifies a host that can be assigned to the network. More host octets means more computers per network.
Each class has a certain range that the first octet can be assigned to. This lets us know to what network class any IP belongs to with ease. Review the diagram below to see a visual diagram.

Now the bad news: you must memorize each range for each class if you hope to pass most network exams. Don’t worry! It’s actually easy- just memorize how we get the numbers, not the numbers themselves! All you have to do is remember n^8 (read as “n” to the eighth power), and how many network portions each class has. Review the diagram below.

One final note before we move on. Notice how we didn’t use the IP address 127 for the class A network- that’s because this is loopback address. We use this for testing configurations on the IP network. Also take note that there are reserved IP addresses, such as those for private networks. These IP addresses will not connect to the internet, which is handy if you just want computers to be connected with each other- and not the whole world.
A Basic Review on Subnetting
The current version of internet protocol, or IP, is IP version 4. This IP version allows four octets of data to represent an IP address. Each octet is considered to be a byte, so there are 8 bits in every octet. Note that in binary form you can see that there are 8 numbers, each one consisting of a bit. Finally, each octet is separated by a period, as shown below.
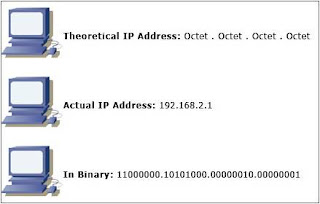
Each IP address is usually represented in decimal form, as seen above as “192.168.2.1”. However, each IP address is actually used by computers in binary form. You may have noticed a huge flaw in IP version 4: the amount of unique IP addresses is limited! To be exact, only 4,294,967,296 unique IP addresses can be created. This may seem like a large number but keep in mind every single device in the world needs a unique IP address to communicate with one another while online.
The IP version 6 protocol was created for when the transition is needed. Most computers don’t use IPv6 just yet, but in the future it will inevitably be used. (In case you were wondering, IPv6 will support 2^128 unique IP addresses… egad!)
How to Subnet a Network
Security sees benefit since the IP addresses of the host computers on each subnet are masked by the network address- which means they are invisible to the outside world. We call this network address translation, or NAT. This same technique helps conserve IP addresses, since all hosts on the subnet essentially just use the network IP address during communication
Do you want to get paid today?
Visit http://www.traxad.com/r/etools_jmezlp
See what our powerful GPT - Get Paid Today Business Model can do for You
Calculating subnet mask
(2^n) – 2 = x
Where “n” is the number of bits you need to borrow and “x” is the number of subnets that will be produced.
You need 5 subnets:
(2^n) – 2 = x
Try 2 first:
(2^2) = 4 and 4-2 is 2 (this is too low)
Try 3 next:
(2^3) = 8 and 8-2 is 6 (this is correct since it will give you 6 subnets)
You have borrowed 3 bits.
So for your example, you would end up with:
199.120.16.0 /21 (since 24-3 = 21)
99 Commands the Windows XP Command prompt can run
Application = Command
Accessibility Controls = access.cpl
Add Hardware Wizard = hdwwiz.cpl
Add/Remove Programs = appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools = control admintools
Automatic Updates = wuaucpl.cpl
Bluetooth Transfer Wizard = fsquirt
Calculator = calc
Certificate Manager = certmgr.msc
Character Map = charmap
Check Disk Utility = chkdsk
Clipboard Viewer = clipbrd
Command Prompt = cmd
Component Services = dcomcnfg
Computer Management = compmgmt.msc
Date and Time Properties = timedate.cpl
DDE Shares = ddeshare
Device Manager = devmgmt.msc
Direct X Control Panel (If Installed)* = directx.cpl
Direct X Troubleshooter = dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility = cleanmgr
Disk Defragment = dfrg.msc
Disk Management = diskmgmt.msc
Disk Partition Manager = diskpart
Display Properties = control desktop/desk. cpl
Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility = drwtsn32
Driver Verifier Utility = verifier
Event Viewer = eventvwr.msc
File Signature Verification Tool = sigverif
Findfast = findfast.cpl
Folders Properties = control folders
Fonts = control fonts
Fonts Folder = fonts
Free Cell Card Game = freecell
Game Controllers = joy.cpl
Group Policy Editor (XP Prof) = gpedit.msc
Hearts Card Game = mshearts
Iexpress Wizard = iexpress
Indexing Service = ciadv.msc
Internet Properties = inetcpl.cpl
IP Configuration = ipconfig
Java Control Panel (If Installed) = jpicpl32.cpl
Java Application Cache Viewer (If Installed) = javaws
Keyboard Properties = control keyboard
Local Security Settings = secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups = lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out Of Windows = logoff
Microsoft Chat = winchat
Minesweeper Game = winmine
Mouse Properties = control mouse
Mouse Properties = main.cpl
Network Connections = control netconnections
Network Connections = ncpa.cpl
Network Setup Wizard = netsetup.cpl
Notepad = notepad
Nview Desktop Manager (If Installed) = nvtuicpl.cpl
Object Packager = packager
ODBC Data Source Administrator = odbccp32.cpl
On Screen Keyboard = osk
Opens AC3 Filter (If Installed) = ac3filter.cpl
Password Properties = password.cpl
Performance Monitor = perfmon.msc
Performance Monitor = perfmon
Phone and Modem Options = telephon.cpl
Power Configuration = powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes = control printers
Printers Folder = printers
Private Character Editor = eudcedit
Quicktime (If Installed) = QuickTime.cpl
Regional Settings = intl.cpl
Registry Editor = regedit
Registry Editor = regedit32
Remote Desktop = mstsc
Removable Storage = ntmsmgr.msc
Removable Storage Operator Requests = ntmsoprq.msc
Resultant Set of Policy (XP Prof) = rsop.msc
Scanners and Cameras = sticpl.cpl
Scheduled Tasks = control schedtasks
Security Center = wscui.cpl
Services = services.msc
Shared Folders = fsmgmt.msc
Shuts Down Windows = shutdown
Sounds and Audio = mmsys.cpl
Spider Solitare Card Game = spider
SQL Client Configuration = cliconfg
System Configuration Editor = sysedit
System Configuration Utility = msconfig
System File Checker Utility = sfc
System Properties = sysdm.cpl
Task Manager = taskmgr
Telnet Client = telnet
User Account Management = nusrmgr.cpl
Utility Manager = utilman
Windows Firewall = firewall.cpl
Windows Magnifier = magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure = wmimgmt.msc
Windows System Security Tool = syskey
Windows Update Launches = wupdmgr
Windows XP Tour Wizard = tourstart
Wordpad = write
Introduction to VOIP Network
VOIP gives solution at almost every layer of the IP network. The Internet Protocol was developed and designed for data communication. The success of the IP network has led to its adaptation to voice networking.
Voice over internet protocol is the fast emerging and replacement technology for the voice communication. Many people still want to know that how it works. Voice over internet protocol costs less than your regular phone service and for this reason it’s more attractive to the consumers. VOIP also costs less than a mobile phone’s monthly cost.
In the fast communication age, the number of the VOIP providers is increasing. As the number of the VOIP providers grows it gives the more options and calling plans. The VOIP service is available for both residential and commercial use that ranges from PC-to-PC service and PC-to-Phone and Phone-to-Phone. The following are the most common and basic features of the VoIP.
VOICE OVER INTERNET PROTOCOL FEATURES
The major feature of the VoIP is that the customers can make call to everywhere in the world. Only the broadband internet connection is required. The customers can take their IP phones with them on the national trips as well as on the International trips. Among the other features of the VoIP are the soft phones, which is a software application that loads onto the computer and is used to make the phone calls. The interface of these softphones is similar to the telephone. By these software phones, anyone call make phone calls to everywhere in the world if broadband internet connection access is available.
The most VOIP services also gives the access and options of call waiting, caller id, call transfer, repeat dialing and three way dialing features. There are some additional features like call filtering, forwarding a call or sending a call to the voice mail, but the service providers may charge additionally for these services. Most VoIP service providers allow the customers to check their voicemail or attached messages to an e-mail by connecting to the web.
The facilities and the components of a VoIP phone system that are supplied by the VoIp providers and phone operators are generally vary with each other. The users should be aware of the pros and cons of the VoIP services before subscribing. Also, the customer should also check the availability of the 24/7 cutomer support that may be required fro the VoIP hardware as well as software configurations and for other technical issues.
How IP Telephony Fits In
Among the other names in the VoIP industry, the Skype and Vonage are the biggest names and all the credit for the growth of VoIP goes to Skype and Vonage. There are a large number of other vendors for the telecommunication industry that have promoted the “IP telephony”. As well as the Cisco Systems and Avaya were two of the earlier names in the VoIP phone system technology. The have paved the way for the growth of VoIP technology. More and more residential customers are using the VoIP service likewise the corporate customers are integrated the IP based-voice technology and upgrading their IP networks to support the VoIP technology. This transition is similar to the move from mainframe computers to the personal computers a couple of years ago
HOW DOES VOIP OVER INTERNET PROTOCOL WORKS
Voice Over Internet Protocol also called Internet Telephony and internet telphony is the technology fo future. With this technology you can make free of cost and very cheap long distance calls all over the world. VoIP uses a broadband Internet connection for routing telephone calls as opposed to the switching and fiber optics. By this process the customer can get the higher efficiency and quality of service as well as low cost. One major and interesting aspect of the VoIP technology is that there is no major infrastructure is required.
The VoIP infrastructure includes the broadband Internet connection, regular telephone line and VoIP software and hardware. Some of renowned companies of the voice over internet protocol business are Vonage and Skype. These both companies prove services to their US people as well as people of the other countries. Cisco systems has also a big name in providing the VoIP hardware.
Get the best VOIP phone installed on your computer and start calling abroad at cheap international rates. VOIP is used by millions of people throughout the world to call abroad at a low cost.
Introduction to the Network Communication Devices
On the other hand if you need to build WAN, you will need to have routers, switches, dedicated or leased telephone lines such as ISDN lines, frame relay connection and other types of wan communication connections.
There are different communication mediums such as Ethernet cables, copper wire, coaxial cable, fiber optic cables, leased telephone lines and ever air is also a communication medium for the satellite communication. The most common networking medium is the LAN is the Ethernet cable (UTP/STP), which is used in the star topology. Hub is a central device of a network and every computer in a network is directly connected with the hub.
If the hub fails to work, the communication between the computers stops till the hub again starts working. Hub broadcasts the data to its every port, and then finding the destined computer, the data sent toward it. The switch is an advance form of the hub similar in functions but the advanced switches has a switching table in them. A advanced switch stores the MAC address of every attached computer and the data is only sent to the destined computer, unlike the hubs where data is sent to all ports. A router is a key device in the internet communication and wan communication system. A router has software called routing table and the source and destination addresses are stored in the routing table.
A router connects two logically and physically different networks. Router finds the IP address of the next hop (next router) and the data is sent toward it and so on. The well known routers developing companies are Cisco systems, Nortel, DLink and others. Every ISP, banks, corporate offices and multinational companies use routers for LAN and WAN communications and communication in their private networks. A gateway can be device or software in a network.
A gateway device connects the LAN with the internet. A gateway is directly exposed to the internet so it should be securely configured and in and out traffic should be monitored. If you are using DSL connection, you must need a DSL modem in your network. The telephone line is connected with the DSL modem and UTP/STP cable attaches your computer with the DSL modem. Modems are the devices that are used to modulate and demodulate the data. They convert analogue signals to digital and digital signals to analogue so that signals can travel on the telephone lines.
There are certain types of the cables that are used to connect two or more computers in a network. Fiber optic cable acts as a backbone between the ISPs and corporate offices. Data travels at the speed of light on the fiber optic cables. The cost and the installation cost of the fiber optic cable is very high but it is becoming very popular in the home networking and LANs also. In the local area networking, 10baseT/CAT5 cable is most commonly in use.
A server is a computer in network that provides services to the client computers such as logon requests processing, files access and storage, internet access, printing access and many other types of services. Servers are mostly equipped with extra hardware such as plenty of external memory (RAM), more data store capacity (hard disks), high processing speed and other features.
WAN Introduction
Put the same scenario if your office has different branches in the same country and different countries. Data communication has become the vital part of the whole computing industry. There are different standards, protocols, devices and applications that form computer network architecture. With the passage of time there are improved standards, communication devices and network applications that make the data communication processor easier. Following is the basic review of the important things that are involved in the data communication system.
TCP/IP
Protocols are the set of rules, agree upon ways and communication standards that computer and devices use to communication with each other. TCP/IP stands for transmission control protocol/Internet protocol. TCP/IP is the standard protocol for network communication in LAN or WAN. All the devices and applications have to follow to same protocols to make network communication system.
Communication Devices
There are certain devices that are used in LAN/MAN/WAN and wireless networking. The most important devices are router, switch, hub, modem, NIC adapter, access points, broadband router and communication cables. Hub/Switch is a centralized device in a LAN and all the computers connect with the Hub/Switch. In case of failure of Hub/Switch the whole communication stops. Router routes the traffic to the destination based on the IP address of the source and destination computer. With the help of the routing table, the router chooses the best short possible path for data to be sent to its destination. Wireless routers and access points are used in the wireless networking.
Types of Networking
There are three main types of the computer networking such as LAN, MAN and WAN. A LAN covers a room or a building. A MAN covers a network in a city and a WAN covers wide areas such as in a city, country or a network between two or more countries. A LAN can be wired or wireless, MAN can be wired or Wireless and WAN can be through wireless communication technologies such as ISDN lines, frame relay and ATM.
Wireless Networking
Wireless networks are replacing the wired networks rapidly. The administrative control becomes less due to the removal of the bundle of cables in wireless network. The key components are wireless router, access points and PCMCIA LAN cards.
OSI Layers Model
To understand the communication process make the data communication process standardized, the ISO developed the OSI (open system interconnectivity, which defines the seven layers of the OSI model. These seven layers include Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link and Physical layer. The detail on the OSI seven layers is covered in the separate topic of this website.
DHCP
DHCP stands for the dynamic host configuration protocol. As we know that a unique IP address is a must for communication in LAN, WAN or internet. Assume you are given the task to assign IP addresses to the 10,000 computers in a network. How would you assign? DHCP answers this questions and it assigns the unique IP addresses to all the computers from a given range. There is an administrative control and you can block, assign, lease, renew, specify duration for the IP address and you also do the many other administrative tasks on the DHCP.
DNS
DNS stands for domain name system. DNS translates (converts) the host name into the IP address and IP address into the host name. One thing is clear that the communication in a LAN private WAN or internet is based on the IP addresses. On internet every IP address is associated with the domain name let’s say assume that the IP address 120.1.1.1. is assigned to www.yahoo.com, 12.1.2.3 is assigned to www.google.com and 35.22.32.5 is assigned to www.msn.com and so on. Just imagine that how many IP addresses you can remember 1, 2, 5, 10, 50, 100 or 1000. IP addresses are actually difficult to remember and domain names are easy so every IP address on the internet is associated with a domain name.
Wi-Fi
Wireless fidelity is a base band wireless networking technology that provides high speed internet connectivity to the offices and home users.
Wi-Max
Wi-Max is an advance broadband wireless network technology that provides very high speed up to 70 Mbps. Wi-Max is designed for the corporate office, roaming and home users.
Internet is an example of Network
Internet is the largest network in the work. Millions of computers from all over the world are internetworked with each other and are the part of the internet. The resources hosted on one computer in one part of the world such as web pages, songs files, graphics, video files, documents and images are accessible to the users in another part of the world.
What is routing?
Routing is consist of two separate tasks.
1. Defining paths for the packets through and internetwork.
2. Forwarding data packets based on their predefined paths.
Generally, there are two types of routing.
STATIC AND DYNAMIC ROUTING
Routing can be performed by manually defining the routes or paths for packets to reach its destination. This is called static routing.
Stating routing works well for the small networks and when using the static routing, the routing table of the each router should be updated each time there is any change in the network configuration or topology. A router, whose routing table is not regularly updated, cannot communicate with the other routers.
While on the other end in most of the networks, routing is accomplished through the use of the dynamic routing. In the dynamic routing, routing protocols, such as RIP, OSPF etc create and maintain the routing tables of each router. Practically, dynamic routing functions very well than the static routing
ROUTING TABLE
A routing table is a set or rules, viewed in a tabular format and this used to define the routes of the data packets. All the network devices, which have IP, enabled functionality such as routers and switches use the routing tables. Routing table stores the information and configurations of every router in the IP enabled network. A routing table contains the information necessary to transmit the packets toward its destination.
When a packet is received, the network devices matches the information contained in the packets and the information in the routing tables and then it defines the shortest possible route for the transmission of the packets towards its destination.
Each packet contains the information of its origin and destination and the routing table contains the following information.
• Destination: The IP address of the packet’s final destination (next hop). Next hop: The IP address to which the packet is forwarded
• Metric: It assigns the cost to each route so that most-effective paths can be picked up.
• Routes: It includes directly attached direct subnets, indirect subnets, that are not directly connected to the device but it can be accesses through one ore more hops
• Interface: The outgoing network interface the device should use when forwarding the packet to its final destination.
Routing tables can be maintained manually by the network administrator or by dynamically (automatically). The static network tables do not change unless the network administrator changes them. Routing tables can be maintained manually or dynamically. Tables for static network devices do not change unless a network administrator manually changes them. In the dynamic routing, the network devices such as routers and switches maintain the routing tables dynamically by using the routing protocols, such as RIP, OSPF etc. In the dynamic routing, the network devices listen and detect any network or devices failure and packet congestions.
Routing in the Internet
Routing is the method in which data finds its destination from one computer to the next. In the Internet there are 3 major aspects of routing.
1. Physical Address Finding
2. Determination of inter-network gateways
3. Numeric and symbolic Addresses
Physical address finding is the method of the Internet Routing and is used when datagram is transmitted from a computer. It is necessary to encapsulate the IP datagram. This encapsulation requires the local network or physical address.
If a computer wishes to transmit IP datagram it needs to encapsulate the physical address of the destination network device in the frame. This address can be achieved by using the table that will map the IP address with the physical address. Such table can be configured into a file that can be read into the memory at the boot up time. Computer normally uses the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which operates dynamically to maintain the translation table.
The second method is necessary because the Internet consists of a large number of local networks, which are interconnected with each other by gateways. Such gateways are known as routers, which has physical as well as logical connectivity with many networks.
The determination of the best suitable gateway and port for a particular IP address is called routing.
The third method generally involves the translation of the human friendly form (names) to the number address (IP Address). IP address can’t be remembered due to its numeric form but the simplest names (domain names) are easy to remember e.g www.yahoo.com, www.google.com, www.msn.com are easiest to remember as compared to the IP addresses 122.11.22.34, 223.45.66.76, 155.44.55.120. DNS translates the domain names into the IP address and IP address into the domain name. This domain to IP translation is a must for communicating on the Internet because communication on the Internet is performed by the IP addresses.
Communication between routers
The Internet is a network of networks. The Internet consists of large number of autonomous systems, each of which further consists of routing domains. Such autonomous systems are usually run by the larger companies or universities. Within the Autonomous system, a router communicates with the other router using the best intra domain routing protocols, which are known as interior gateway protocols. Autonomous system are connected via gateways, these exchange information using inter domain routing protocol, which are also called exterior gateway protocols.
The RIP or (Routing Information Protocol) is the commonest interior gateway protocol and the recent protocol such as open shortest path first (OSPF). The purpose of these protocols is to enable routers to exchange locally so that all the routers in the autonomous system must a have coherent and up to date information.
When a host receives the new routing information, it is likely to update not only to it but also sends this new updated information to all the connected hosts so that they can updated themselves. Hence these changes propagate across the entire network.
GSM Introduction
GSM leads the world as the fastest growing mobile/wireless digital technology that is most reliable and is available in the marketplace today. GSM provides the integrated high-speed data, fax, voice mail, paging and short messages services features. GSM offers the secure communication, privacy and fraud prevention.
After subscribing to the GSM service, you can use your phone at your home, office, across the continent or around the world with the country specific SIM cards. GSM operates on the different frequency levels like 900 MHz, 1800 MHz or 1900 MHz.
1900Mhz is used in the North America and 1800 MHz is for the other locations. Different mobile phone networks around the world operate at different frequencies. If you wish to use your mobile phones outside of your GSM frequency range then you should use a mobile/handset that support multiple frequencies. Before buying a mobile phone, make sure that it is compatible with the different bands of the GSM.
Dual-band – A dual band phone operates at different spectrum like 900 MHz and 1800 MHz. Dual-band GSM works in Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia and Sound America.
Tri-band – A tri band phone operates on the three different frequency levels like 900 MHz, 1800 MHz and 1900 MHz. This means that you can use your mobile phone in Europe, Asia, Australia, Africa and North America.
Quad-band – A quad band GSM capable phone allows you to roam almost everywhere in the world. It covers the different frequency ranges like 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz and 1900 MHz. 99% countries in the world use the GSM standard and it seems that GSM will eventually be the only cell phone standard in the mobile communication world. GSM provides the best voice quality and standard.
Today, there are more than 720 GSM mobile networks across the more than 214 countries. According to the recent statistics, there are more than 2 billion users of the GSM in the world. Major GSM using countries includes China, Russia, United States and India. A mobile phone can be a bewildering affair for a traveler. It is mostly incompatibility with the network of your visiting country, since every country in the world has different frequency band of operation. With a GSM enable mobile phone you can access more than 214 countries around the globe.
GSM is a state of the art technology offering voice, data, fax and SMS capabilities. Most of the mobile phone operators now offers email to SMS service by which you can receive the important news, flight status and other useful information on your mobile phone. Many operators give access to the ISDN services by which fast data transmission is possible. Many other offers GPRS (Global Packet Radio Service) with this service you can connect to the high speed data communication channel like 9600 bps. The two major GSM service providers in the US are the T-mobile and Cingular.
Computer Networking Topologies
• bus
• star
• ring
• mesh
• Tree.
Hybrid networks are the complex networks, which can be built of two or more above mentioned topologies.
Bus Topology
Bus topology uses a common backbone to connect all the network devices in a network in a linear shape. A single cable functions as the shared communication medium for all the devices attached with this cable with an interface connector. The device, which wants to communicate send the broadcast message to all the devices attached with the shared cable but only the intended recipient actually accepts and process that message.
Ethernet bus topologies are easy to install and don’t require much cabling and only a main shared cable is used for network communication. 10Base-2 and 10BaseT are two popular types of the Ethernet cables used in the Bus topology. Also, Bus network works with very limited devices. Performance issues are likely to occur in the Bus topology if more than 12-15 computers are added in a Bus Network. Additionally, if the Backbone cable fails then all network becomes useless and no communication fails among all the computers. Unlike in the Star topology in which if one computer is detached from a network then there is not effect on the other computers in a network.
Ring Topology
In ring Network, every computer or devices has two adjacent neighbors for communication. In a ring network, all the communication messages travel in the same directory whether clockwise or anti clockwise. Any damage of the cable of any cable or device can result in the breakdown of the whole network. Ring topology now has become almost obsolete.
FDDI, SONET or Token Ring Technology can be used to implement Ring Technology. Ring topologies can be found in office, school or small buildings.
Star Topology
In the computer networking world the most commonly used topology in LAN is the star topology. Star topologies can be implemented in home, offices or even in a building. All the computers in the star topologies are connected to central devices like hub, switch or router. The functionality of all these devices is different. I have covered the detail of each networking devices in the separate portion of my website. Computers in a network are usually connected with the hub, switch or router with the Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) or Shielded Twisted Pair Cables.
As compared to the bus topology, a star network requires more devices & cables to complete anetwork. The failure of each node or cable in a star network, won’t take down the entire network
as compared to the Bus topology.
However if the central connecting devices such as hub, switch or router fails due to any reason,then ultimately all the network can come down or collapse.
Tree Topology
Tree topologies are comprised of the multiple star topologies on a bus. Tree topologies integrate multiple star topologies together onto a bus. Only the hub devices can connect directly with the tree bus and each Hub functions as a root of a tree of the network devices. This bus/star/hybrid combination supports future expandability of the computer networks, much better than a bus or star.
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology work on the concept of routes. In Mesh topology, message sent to the destination can take any possible shortest, easiest route to reach its destination. In the previous topologies star and bus, messages are usually broadcasted to every computer, especially in bus topology. Similarly in the Ring topology message can travel in only one direction i.e clockwise or anticlockwise. Internet employs the Mesh topology and the message finds its route for its destination. Router works in find the routes for the messages and in reaching them to their destinations.The topology in which every devices connects to every other device is called a full Mesh topology unlike in the partial mesh in which every device is indirectly connected to the other devices.
Summary
Topologies are the important part of the network design theory. A better network can be built if you have the knowledge of these topologies and if you know the difference between each topology. Similarly you should have the knowledge of each network device so that you can properly use them according to your network needs. A misconfigured network can result in a waste of time and energy as well as a lots of troubleshooting methods to resolve the issue. So thebasic understanding of the network topologies and network devices is a must to build a good network.
Recovery of data.
IT Administrator should know about all the possible security attacks and also know their solutions. IT Administrator should look for the viruses from the Internet, Malware, Adware, Trojan horses, E-mail attachments, Floppy disk, CD or any infected computer that is attached to the network. Spyware and network intrusions are specifically designed to get the secret information from their target companies, which can do harm for the company. Everyday security threats are refined as hackers designed new security threats.
The main cause of a security threat in the small companies is the misuse of the internet without proper anti virus, anti spyware installed on the every PC of the company’s network. For example if a company’s employees browse an inappropriate website, sends or receives the infected data, leaks company’s secret information, then there are greater chances for a possible virus/malware attack.
In my opinion, the end user’s education on the security threats, preventions and precautionary measures are must. They should be trained about the possible and easy virus attacks from the internet if they browse the inappropriate sites.
Another important thing is the insider’s attack e.g if the company’s employee leave the company for any reason, then its very important that all the computer and other company’s sensitive assets access should be revoked by him immediately. I have personally seen a situation, when a company’s network administrator was dismissed and he access the company’s server by VPN and send harmful viruses to the server and the entire computer network, and it was impossible for the IT manager to control all the security attacks in one time.
It’s the responsibility to keep a closer eye on the new employee’s activities, their access to the sensitive data, and computers servers. IT managers should bring it in the knowledge of the employees that any change in their computer will be logged. So that nobody can even try to do anything that is not permitted.
There are six basic security steps for the Windows platforms. If a network administrator can follow these steps then he/she can save the computerss from all the possible security threats and virus or malware attacks.
First the IT managers should divide the computer network into the segments. They should filter the access to the internet with the help of a firewall by blocking TCP port 1433 and TCP port 1434. Internet access from the outside should be allowed to the SQL systems. All the unwanted ports should be blocked and only the required ports should be open for access.
Second, moderate the affect of the spoofed ports. The port 80 is the most commonly used port.
Third, as network administrator you should install the current patches to you’re your server computer and client’s up to date. Patches can prevent the systems from the known vulnerabilities. Latest patches can be downloaded from the Windows website. You can also configure to automatically update. Also third party patches products are also available that can be tested and installed. Additionally, by strengthening the user authentication process can be very helpful for security purposes.. You can use password security and other technological methods for the authenticate purpose.
Fourth, you can limit the number of the network administrators it can also be helpful for security a computer network. Admin rights should not be given to the local PC, until and unless it is the requirements for the applications that are installed on the local PCs.
Fifth, protect computers against the known attacks. Don’t disable any Windows known service such as clipbook, Telnet etc. Set the powerful permission the shared network resources.
Last, you can configure the security policies. Implement the security policies on your network.
Security measures and methods have expenses with their purchases. Deployment, maintenance and the implementations of these methods can increase the security cost. Some other things which a IT administrator or a IT manager should keep in mind are the education of the employees about the computer networking, security, use of the encryption and digital right management software, block the unwanted emails and audit security on the regular basis. Network security methods should be used and implemented in order to prevent your computer network from the unauthorized access.
In this article you have discovered the Computer Network Security Overview More topics to come are Cisco Labs, Routing, IP addressing & Free IT resources.
windows xp networking
2. After the system detect any new hardware device (NIC adapter), it will search for the appropriate driver. In case if Windows XP doesn’t find the driver you will be promoted to install the driver for that device.
3. When the driver for the NIC adapter is successfully installed, go to the Start > Control Panel > double click Network Connections >. Here you will see Local Area Connection Icon with the lights turned on.
4. Right click the Local Area Connection > Properties > Internet Protocols > Properties. Here you can assign an IP address manually or obtain an IP address automatically from the DHCP server. Here you can also configure the subnet mask, Gateway and DNS.
How to add a computer in your network using Windows XP
Windows XP is designed for the standalone computers as well as for connecting with the other computers in the network. After connecting to the network, you can share files, send printing requests, access internet, play LAN games and share CD/DVD ROM of the server. You can add your computer in the network by the following method.
1. Turn off your computer
2. Log on as a Administrator and add a LAN card into the PCI slot of your computer
3. You will be prompted for the driver for the LAN card. Install the driver by CD-ROM, floppy or through the USB drive.
4. After installing the driver of the LAN card, you are required to configure it. You can configure the LAN card as mentioned in this section.
How to connect an Xbox to your network
To connect both the Xbox and computer to the internet you need to have X-box Live compatible router. Router will share your internet connection so that your computer and Xbox use the internet connection at the same time. To connect Xbox to your network, connect it to your TV.
1. Unplug the network cable from the back of your computer and plug it into the port WAN, Internet or WLAN on the back of your router.
2. If your computer is not currently connected to the internet, plug one end of the cable into the Modem and the other end of the cable into the WAN, Internet or WLAN port of your wireless router.
3. Plug in your router, after a minute or two the WLAN, WAN or internet light on your router should be turned on.
4. Plug your computer’s network cable into the router.
5. Turn off your Xbox 360. Connect it to the internet by plugging one end of the network cable included with Xbox 360 into the router and the one end into the I/O port at the back of the Xbox 360.
6. Start your Xbox 360 and start your gamer profile. You can enjoy both Xbox 360 and Xbox live play.
How to share and stop sharing files
To share files and folders on your computer and on the other computer on the network you need to have Administrative rights and you need to share a folder on your computer and setup user accounts.
1. Log on with an Administrator account
2. Open my computer > drive click on any drive (C, D, F) and open it. Select the folder you want to share.
3. Right click on that folder >Go to sharing and security >. In the network sharing and security. Check “share this folder on the network” and assign a shared name to this folder. You can also allow rights to the other users on the network by checking this box “Allow network users to change my files”.
How to Map a Network drive
1. Open Windows explorer by right clicking on the Start > Select any folder you want to map for a network drive > go to tools > Map network drive > Assign a drive letter and select the folder, which you want to map. You can open all the Mapped drive folders through the My Computer.
How to backup your Network Settings
Windows XP has a handy utility by which you can backup your network settings and restore them at any time.
Backup your Network Settings
1. Start > Accessories > System Tools > Backup. Welcome to Backup or Restore wizard will appear.
2. On the backup and restore page, make sure backup files and settings is selected.
3. On what to backup page, select let me choose what to backup and click next.
4. Expand my computer on the items to backup page and select system state. You can backup your files and folders at the same time by selecting those folders.
5. Click the browse button and select the backup destination with at least 1500 MB free available space. You can save the backup to the my documents folder if you are only taking backup of your network settings.
6. After completing the backup process click finish.
How to repair Network Connections
Windows XP can troubleshoot many configurations and software related problems with any third party tool. You can repair your network connection the by following steps.
1. Control Panel > Network and Internet Connection > Double click network connections and right click on the Local Area Connection and click repair. It will repair the network connection for any connectivity related and other problems.
How to ping a Local Area Network
If you want to ping any computer in your local area network or WAN you can ping the computer with the following command. Ping is used to check the connectivity of any computer.
Ping IP Address of the Computer
Ping 10.10.10.100
If you get reply from that computer, that shows network connectivity is okay.
Message “Reply from 10.10.10.100: bytes=32 time <1ms TTL=128”
If you get the time out message like the following then there is problem in the network connections. Check the IP addresses cables connectivity at both ends to troubleshoot this problem.
Message “Request Time Out”
Easy Way to Subnet
On the second from the top left hand row write 128 then add 64 to make 192 then add 32 to make 224…all the way down to 255.
Here is the chart written out in full:
http://www.subnetting-secrets.com/subnetting_cheat_sheet.html
Selecting The Right Cisco Training Online Examined
The sort of jobs available with this type of qualification mean it's likely you'll end up working for large companies that have multiple departments and sites but need to keep in touch. On the other hand, you might end up joining an internet service provider. Both types of jobs command good salaries.
Getting your Cisco CCNA is what you should be aiming for - at this stage avoid being tempted to do the CCNP yet. Once you've worked for a few years you will know if CCNP is something you want to do. Should that be the case, you'll be much more capable to succeed at that stage - because you'll know so much more by then.
If an advisor doesn't dig around with lots of question - the likelihood is they're just trying to sell you something. If they push a particular product before looking at your personality and experience, then it's very likely to be the case.
Where you have a strong background, or sometimes a little live experience (some industry qualifications maybe?) then it's more than likely your starting point will be different from someone with no background whatsoever.
Starting with a basic PC skills program first is often the best way to commence your IT training, but depends on your skill level.
All programs you're considering has to build towards a nationally (or globally) recognised accreditation as an end-goal - not a useless 'in-house' piece of paper.
You'll find that only recognised examinations from the top companies like Microsoft, Adobe, Cisco and CompTIA will have any meaning to employers.
Being a part of the information technology industry is one of the most thrilling and changing industries that you could be a part of. To be dealing with leading-edge technology is to do your bit in the gigantic changes that will impact the whole world for generations to come.
There are people who believe that the revolution in technology that's been a familiar part of our recent lives is cooling down. There is no truth in this at all. Terrific advances are ahead of us, and the internet in particular will be the biggest thing to affect the way we live.
And don't forget salaries moreover - the typical remuneration in the United Kingdom for a typical IT professional is a lot greater than average salaries nationally. Odds are you'll make a whole lot more than you'd expect to earn doing other work.
There is a significant national requirement for trained and qualified IT technicians. It follows that as growth in the industry shows little sign of contracting, it is likely this will be the case for the significant future.
Potential trainees hopeful to kick off a career in computers and technology generally have no idea of what direction to consider, or which area to obtain accreditation for.
After all, if you've got no know-how of IT in the workplace, how could you possibly know what someone in a particular field actually does day-to-day? How can you possibly choose which educational path provides the best chances for a successful result.
The key to answering this quandary properly stems from an in-depth discussion of several different topics:
* Your personality can play a starring part - what gives you a 'kick', and what are the areas that ruin your day.
* What is the time-frame for the retraining?
* Is your income higher on your wish list than some other areas.
* Understanding what the normal job areas and markets are - including what sets them apart.
* You will need to understand the differences across each individual training area.
For most people, considering so much data needs a long talk with a professional that can explain things properly. And we don't just mean the accreditations - but also the commercial requirements also
Tuesday, January 26, 2010
A CCNA Certification Validates Advanced IT Skills
What is a CCNA certification?
CCNA stands for the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification. It is the entry-level certification of Cisco. Such is a pre-requisite for the other higher levels of Cisco certifications.
Basically the CCNA certification is the first step towards the series of Cisco IT certifications. It is best suited for IT help desk engineers, field technicians, computer networkers, and other IT professionals involved in managing the processes of computer networks.
What is the next step after getting a CCNA certification?
After an IT professional has gained the CCNA certification, he can then move forward and acquire the other Cisco Certifications. These include the CCNP (Cisco Certified Network Professional) certification which is designed for network administrators and network technicians; and CCIE (Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert) certification which is tailor made for senior network administrators and high level positions.
What are the topics that are included in the CCNA certification exam?
An individual aspiring for a CCNA certification should be knowledgeable with the basic history of networking. He should also be able to identify and utilize the OSI reference model and the basic principles used in network designs. Also, he should be able to construct and design both local-area networks (LANs) and wide-area networks (WANs). Knowledge on Ethernet and VLANs is also necessary as well as skills in IP addressing, and knowledge on TCP/IP protocols (ARP, RARP, BOOTP, and ICMP).
Moreover, the aspiring candidate should be proficient with routers and routing protocols, bridges, and switches. He should also be an expert with the Cisco IOS (Internetwork Operating System) and lastly, he should have prime knowledge on computer network management and security.
What other things should an aspiring CCNA know?
There are no pre-requisite tests for getting CCNA. Generally, the exam for the CCNA certification will last for two hours as it is only comprised of seventy eight questions.
In order to pass the exam, the aspiring candidate should be able to answer at least sixty three questions correctly. Also, before any individual can take the certification exam, he is required to pay an average of a hundred dollars as exam fee. Once the aspiring candidate pass, the results will be valid for three years. However, an official recertification exam should be taken at the end of the validity period.
How can one be prepared for a CCNA certification exam?
The aspiring individual should be able to get hands-on experience with computer systems, as well as formal IT trainings. In addition to that, an individual can opt to find an official Cisco Learning Partner. Such organizations will offer aspiring candidates with “live” preparation courses and materials.
If an IT professional cannot avail of actual training courses, he can study for the CCNA certification exam using books and online sources. Aside from step-by-step tutorials and lectures, an aspiring candidate can access comprehensive practice exams for the CCNA certification. In doing so, he can assess his present knowledge and capability to be CCNA certified.
TIPS FOR A SMOOTH RUNNING SYSTEM
Things you should NOT do
------------ --------- --------- --
1: Use Internet Explorer (1)
2: Use any browser based on Internet Explorer (e.g. Maxathon and MSN Explorer)
3: Use Outlook or Outlook Express (2)
4: Open email attachments you haven't manually scanned with your virus scanner
5: Open email attachments you were not expecting, no matter who they appear to be from
6: Respond to spam messages, including using unsubscribe links
7: Visit questionable websites (e.g. porn, warez, hacking)
8: Poke unnecessary holes in your firewall by clicking "Allow" every time some program requests access to the Internet (3)
9: Click directly on links in email messages
10: Use file sharing or P2P programs
11: Use pirated programs
Things you SHOULD do
------------ --------- --------
1: Use a non-IE or IE based browser (4)
2: Always have an up to date virus scanner running (5)
3: Always have a firewall running (6)
4: Install all the latest security updates (7)(8)(9)
5: Delete all unsolicited emails containing attachments without reading
6: Manually scan all email attachments with your virus scanner, regardless of whether it's supposed to be done automatically
7: Copy and paste URLs from email messages into your web browser
8: Inspect links copied and pasted into your web browser to ensure they don't seem to contain a second/different address
9: Establish a regular backup regimin (10)(11)
10: Make regular checks of your backup media to ensure it is still good (12)
Being a considerate Internet user & other misc tips
------------ --------- --------- --------- --------- --------- -
1: Do not send attachments in emails (13)(14)
2: Do not use stationary or any other kind of special formatting in emails (13)
3: Do not TYPE IN ALL CAPS (15)
4: Avoid texting speak or "l33t speak" (16)
5: Do not poke the sleeping bear (17)
Notes
--------
(1) Sadly sometimes this is unavoidable, so only use IE when the site absolutely will not work with any other browser and you cannot get that information/ service anywhere else, and only use IE for that one specific site.
(2) Outlook and Outlook Express are very insecure, and basically invite spam. The jury is still out on Vista's Windows Mail, but given Microsoft's history with email programs, extreme caution is advised. Possible replacements include Mozilla Thunderbird, Eudora, The Bat, and dozens of others.
(3) When it doubt over whether or not to allow some program, use Google to find out what it is and whether or not it needs access to the Internet. Otherwise, denying access is the safest course of action, since you can always change the rule later.
(4) On Windows your options include: Mozilla Firefox, Seamonkey, Opera, Flock, Chrome, and Safari. I would personally recommend Firefox with the NoScript extension for added security, but it the important thing is to pick one and use it instead of IE.
(5) AVG Free and Avast are available if you need a decent free virus scanner
(6) XP/Vista's firewall is probably good enough for 99% of all Windows users, but other options include ZoneAlarm, Outpost Firewall, and Comodo. If you have a router with a firewall built into it, there is no need for any of the aforementioned firewalls to be running.
(7) Microsoft's usual system is to release security updates every second Tuesday of the month.
(8) Use of Windows Update on Windows operating systems prior to Windows Vista requires Internet Explorer, and is thus a valid exception to the "No IE" rule.
(9) Service packs should ALWAYS be installed. They frequently contain security updates that will ONLY be found in that service pack.
(10) You can go with a full fledged backup program, or simply copying important files onto a CD/DVD/Flash drive.
(11) I'd recommend a tiered backup system. For example, you might have 5 rewritable DVDs, and every day you burn your backup onto a new disc. On the 6th day, you erase the disc for Day #1 for your backup, and so on so that you have multiple backups should one disc ever go bad.
(12) Replace rewritable CDs and DVDs approximately every 3-6 months.
(13) These dramatically increase the size of email messages (2-3X minimum) and clog up email servers already straining to cope with the flood of spam pouring in daily.
(14) If you want to share photos with friends/family, upload them to some photo sharing site like Flickr or Google's Picasa Web and then send people a link to that particular photo gallery.
(15) This is considered to be the same as SHOUTING and many people find it to be hard to read along with highly annoying.
(16) Unless the goal is to make yourself look like a pre-adolescent girl, or someone overcompensating for their gross inadequacies, and you don't want people to take you seriously.
(17) Most REAL hackers are quite content to leave you alone unless you make them take notice of you. No dinky little software firewall or consumer grade router is going to keep them out of your system. So do not go to some hacker website or chat room and start shooting your mouth off unless you're prepared to accept the consequences
------------ --------- --------- --------
http://www.siteadvi sor.com/
and some redundancy like windows defender and:
http://www.microsof t.com/security/ malwareremove/ default.mspx
Sometimes one is not enough. A second may catch what the first one doesn't. Use these when you think your in trouble. Use the others, the ones you've mentioned for routine scans. Better safe then sorry.
------------ --------- --------- -------
The only thing I see missing is a firewall. I know that the Avast Free Edition has what they call a 'lightweight' firewall which they name "Network Shield", so I assume that is what you have, and it is running.
This is what they say about it;
"Network Shield
A new resident protection module was added to avast! 4.5: the Network Shield. This module provides protection against known Internet worms/attacks. It analyses all network traffic and scans it for malicious contents. It can be viewed as a lightweight firewall (or more precisely, an IDS (Intrusion Detection System). "
If that's what you have, then you're pretty well covered. I don't know how well rated that lightweight firewall is.
But other than that, you're looking OK. Just some other things to help, (if you don't mind more such information) ;
1] Email. Don't preview 'suspect' email. Just delete. Don't open email attachments immediately, save to disk first, then scan with Avast. Never post email addresses in forum posts or other non-secure web sites.
2] If you are using IE, consider switching to Firefox, or some other browser. IE is still the most vulnerable of browsers. Firefox has a useful add-on called WOT, (World of Trust), that marks web sites with green to red icons, green for good, red for warning.
3] No P2P file sharers. Apart from the obvious copyright problems with downloading pirated files, all too often such files have malware.
